- Roko's Basilisk
- Posts
- The Race To Replace Search As We Know It
The Race To Replace Search As We Know It
Plus: Talking cars, vape-peddling avatars, and an email-driven startup chasing agentic AI.
Here’s what’s on our plate today:
🌐 AI browsers vs. Google—why Dia, Comet & friends might upend search.
⚡ Faraday’s smiley-grille e-van and metaverse avatars peddling smokes.
🧠 One-click AI summary → instant mini-PRD (ditch the tab-hopping).
❓ What’s your biggest worry about an AI-first web?
Let’s dive in. No floaties needed…

Guidde—Create how-to video guides fast and easy with AI.
Tired of explaining the same thing over and over again to your colleagues? It’s time to delegate that work to AI. Guidde is a GPT-powered tool that helps you explain the most complex tasks in seconds with AI-generated documentation.
Share or embed your guide anywhere
Save valuable time by creating video documentation 11x faster
Simply click capture on the browser extension and the app will automatically generate step-by-step video guides complete with visuals, voiceover and call to action.
The best part? The extension is 100% free.
*This is sponsored content

The Laboratory
How AI is Redefining Online Search and Content Discovery
2022 was the year artificial intelligence entered public consciousness; since then, we have seen AI companies push to integrate their generative capabilities in products for both individuals and organizations. A dramatic shift in the push for AI integration has come in the form of agentic AI, or tools capable of performing tasks with little to no human intervention. And these tools are finally making their way to users in the form of AI browsers.
Back in June, the Browser company launched its latest browsing tool called Dia. The browser was created with the idea that traditional web browsing tools would eventually give way to AI-powered tools. The idea relies on the understanding that as users adopt tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude, they would rely on AI-generated summaries for information, rather than visiting individual websites. Since then, we have news of OpenAI prepping its browser, and Preplexity launching its Comet browser for users.
Even though OpenAI has yet to officially release a browser, Dia and Comet, at their core, are live examples of AI tools challenging Google’s Search dominance. And the challenge is more imminent than was earlier thought.
AI browsers challenge Google’s search dominance
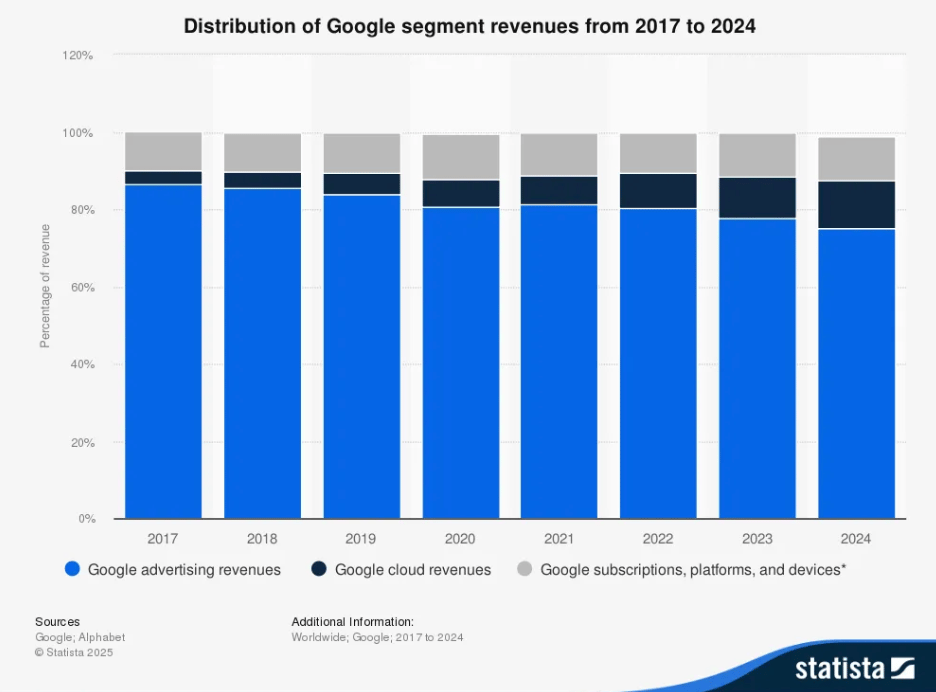
In April, Google searches on Apple’s Safari browser declined for the first time in nearly two decades. While this may not seem like a big deal, especially for a company that controls nearly 90% of the market share, investors did not take it lightly. When the news came out, Alphabet’s share price fell by around 7%. The shift has been so dramatic that people have started using the term “ChatGPT-ed,” instead of Googled, Gil Luria, an analyst at US-based financial services company DA Davidson, told The Observer.
Google has been a dominant player in the Search market, which has made it highly profitable. However, the company is now facing increasing regulatory scrutiny in the U.S. and the EU, which may be part of why it seems to be playing catch-up with new entrants.
At its annual developers conference, Google CEO Sundar Pichai said the company’s in-house large language model, Gemini, would be embedded in many of its search products. Pichai also said that a new “AI mode” would reimagine the way its Search tool works.
However, the challenges for Google go deeper than mere AI tools.
Google generates most of its profits through AdWords-based search. Although the exact mechanics of how ads are ranked and shown to users aren't fully disclosed, it's understood that Google conducts a 'smart auction.' In this auction, advertisers bid to display their ads, and the highest bidder wins but pays only slightly more than the next highest bid. This process helps users find relevant results, while also driving significant revenue for Google.
Besides sponsored search, Google also offers organic search based on search terms. This helps to ensure that users stick to Google’s platforms like Search, YouTube, News, and Maps.
This is where businesses work hard to optimize their online presence through Search Engine Optimisation (SEO), in a bid to ensure they are visible on the first page and the first few slots of organic search results on Google Search. And though it may not be an ideal situation, it has shaped how businesses strategize their online presence. However, generative AI tools could rewrite the playbook.
How AI browsers are transforming user behavior
With more users turning to AI-powered tools for information, fewer are opening web browsers with the default Google search engine anymore. In this scenario, tools like ChatGPT, the search engine in Deepseek, Copilot from Microsoft, Dia from The Browser company, and Comet from Perplexity will become the favored choice. And AI companies know this, evidenced by their shift towards launching browsers capable of more than just searching for information.
For Google, so far, the absence of advertisements in the AI tools has been a blessing. However, generative AI tools are not cheap, and with advertisements being the primary source of revenue for most consumer internet services, AI companies are looking at them as a viable option.
In December 2024, a report from the Financial Times said that OpenAI was weighing an ads business model, and that though there were no active plans to pursue advertising, the idea was being considered.
Once generative AI tools start allowing advertisers to target users, the very foundation on which online advertising works could undergo an overhaul.
As for users looking for organic results, the search might become even more challenging.
Potential pitfalls of AI-driven browsing
As users move towards AI tools for information, organizations are also expected to shift their strategies to ensure they have their users’ attention. A central concern is what happens if website owners insert keywords in their content to make sure AI-powered browsers or search engines surface their pages more often, potentially at the expense of high-quality, user-focused content.
Another concern is that website owners might start using AI-generated content tailored specifically to satisfy algorithms rather than actual human readers. This approach could lead to repetitive, superficial, or spam-like content, harming both user experience and the credibility of AI-generated responses.
The interesting bit is that Google spent decades indexing vast swathes of the internet to combat these very issues. And AI companies know this.
Google, Perplexity, and OpenAI have each introduced safeguards, such as algorithm updates, content filtering, and human-feedback loops, to combat keyword stuffing and duplicated AI-generated content. However, as was seen in the past, it is not an easy task. As AI companies strengthen their guardrails, new practices emerge to hoodwink the algorithms.
Will AI completely transform online search?
As users' habits undergo the transition from hunting for information on listed websites online to asking an LLM-powered AI tool to do it for them, we are likely to see more AI browsers hitting the shelves.
And as the competition to become the default browser intensifies, AI companies will continue to push more powerful tools. However, while the race heats up, questions around monetization, inorganic content, and content designed for mere ingestion by LLMs flooding the online space cannot be brushed under the carpet. And if they are, we may risk turning the internet into an information wasteland that users will struggle to navigate.


Brain Snack (for builders)
 | 💡 Turn a “how-to” explainer into a living product brief.1. Ask your AI browser to summarize three competing tutorials on the feature you’re planning.2. Prompt it to extract: problem statements, user pain points, and success metrics.3. Paste the bullet summary into your roadmap doc as a “mini-PRD.”Result: you replace hours of tab-hopping with one condensed artifact that everyone on the team can riff on—no extra tooling required. |

Nail your narrative and connect with your audience with MasterClass.
Learn storytelling from Michael Lewis, #1 New York Times bestselling author of Moneyball, The Big Short, and Going Infinite, as he reveals how to turn complex ideas into captivating narratives.
In MasterClass's “Tell a Great Story,” Lewis teaches you how to structure a story, connect with audiences, and make anything—books, speeches, even small talk—compelling.
Find your voice with his real-world examples and storytelling secrets, and unlock 200+ more classes taught by the world’s best with MasterClass!
*This is sponsored content

Quick Hits, No Fluff
Faraday Future’s “FX-Van” concept — electric delivery van sports an AI-powered LED “face grille” that chats with pedestrians and drivers alike.
Big Tobacco infiltrates the metaverse — watchdogs find kid-friendly avatars handing out virtual cigs and vapes, sparking fresh calls for VR regulation.
Inbox as agent HQ — stealth startup claims linking AI agents directly to email threads slashes hallucinations and boosts enterprise adoption.

Wednesday Poll
🗳 Would you switch from Chrome to an AI-first browser if it handled searching, summarising, and checkout for you? |

Meme of The Day


Rate this edition
What did you think of today's email? |



